Testosterone is an anabolic steroid responsible for promoting the repair and growth of muscle proteins. Currently, there are a lot of half-truths out there regarding low testosterone levels among men and how to raise them. To help clarify some of the misinformation being propagated, here is what you need to know about low-T and what you can do about it in the gym.
Testosterone-boosting Workout
Have you noticed the recent onslaught of TV commercials touting the hazards of the fabricated syndrome of low testosterone? Testosterone (T) is an anabolic steroid responsible for promoting the repair and growth of muscle proteins. To help clarify some of the misinformation being propagated, here is what you need to know about low-T and what you can do about it in the gym.
1. After the age of 35, men naturally start to produce 1 to 3 three percent less T per year, unless they do something to elevate production of the hormone. The good news is that the right exercise program can help men reduce the loss of T and actually increase production well into their later years
2. The body produces T as a response to resistance training, because it helps repair damaged muscle proteins and promotes the growth of new muscle tissue. Heavy resistance training for the larger muscle groups can elevate the amount of T immediately after exercise. However, an extended period of resistance training is necessary to increase the levels of cell receptors that work with T to promote the growth of muscle proteins.
3. Workouts to increase T should focus on multijoint compound movements for large muscle groups combined with short rest periods. For best results, the overall duration of the workout should be relatively short (45 minutes or less) and the training session should focus purely on strength with no cardio training.
4. Often the most overlooked variable of any exercise program is the post-workout recovery period. The actual workout is only part of the equation responsible for muscle growth. Adequate recovery is important to allow T to repair and rebuild muscles used during the workout. For best results, make sure you do your heavy workouts on days when you can get a full night’s sleep because the body produces T during the REM cycles of sleep.
The following workouts can help men increase T levels naturally without the need for expensive hormone replacement therapy. Using moderate to heavy weights for eight to 10 repetitions (with fatigue occurring by the last rep) per exercise can provide the requisite damage to muscle protein that signals the production of testosterone.
Here is an optimal workout schedule for T production: resistance training on day one, low-to-moderate intensity steady-state cardio on day two and bodyweight training such as yoga or calisthenics on day three. Allow a complete rest day at least once a week. Alternate workouts A and B on the resistance-training days, and make sure to do a complete dynamic warm-up before performing the strength-training exercises. Finally, allow at least two complete days of no heavy strength training before performing another weightlifting session.
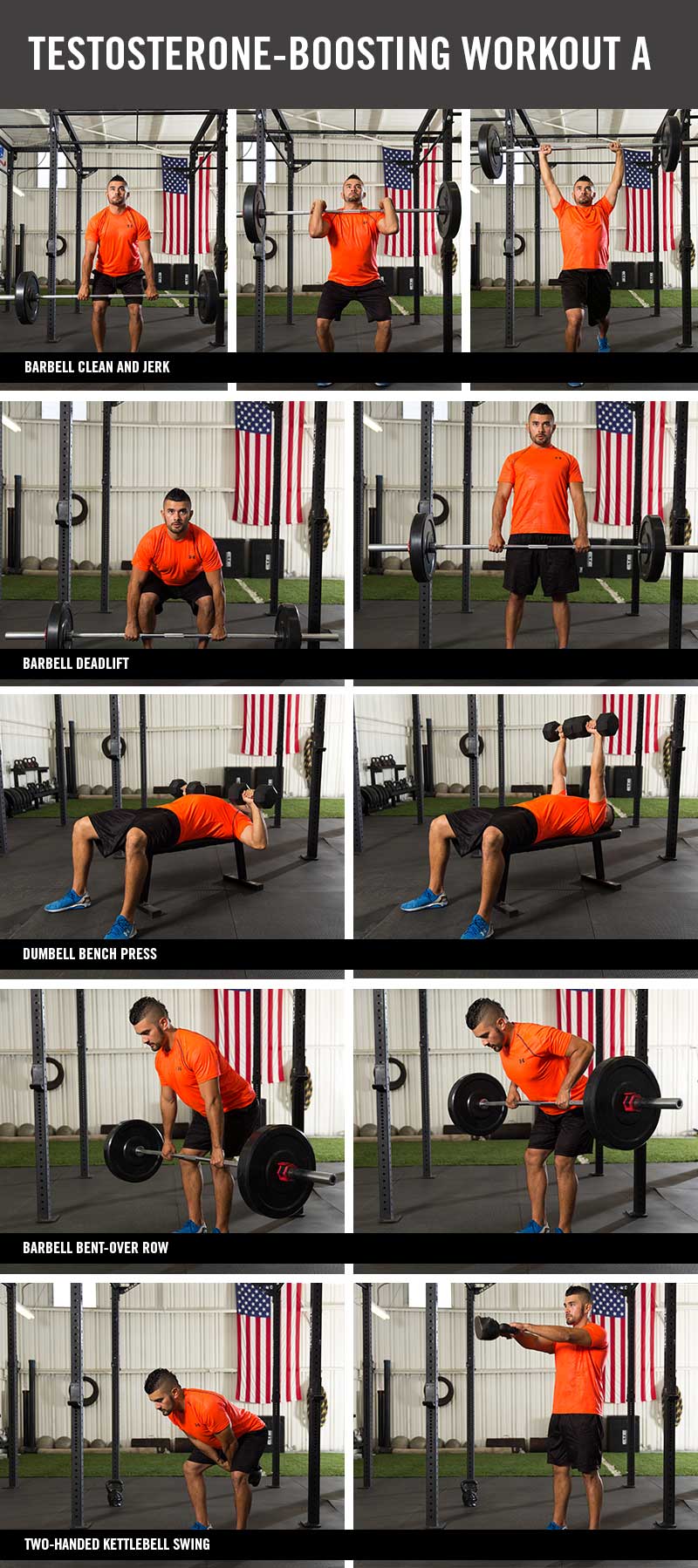

Testosterone-boosting Workout A
Exercise: Barbell clean and jerk*
Intensity+: 8-10 RM
Reps: 4-6
Tempo #: Explosive
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4
Exercise: Barbell deadlift
Intensity+: 8-10 RM
Reps: 8-10
Tempo #: Moderate
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4
Exercise: Dumbbell bench press
Intensity+: 8-10 RM
Reps: 8-10
Tempo #: Moderate
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4
Exercise: Barbell bent-over row
Intensity+: 8-10 RM
Reps: 8-10
Tempo #: Moderate
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4
Exercise: Two-handed kettlebell swing
Intensity+: 10-12 RM
Reps: 10-12
Tempo #: Explosive
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4
- Intensity: Perform 8-10RM and use a weight that can be lifted for a maximum of 8 reps. If it is possible to do more, increase the amount of weight used.
- # Tempo – This refers to the speed of movement. With the exception of the kettlebell swing and the barbell clean and jerk, the movement speed should be one to two seconds in each direction.
For the barbell clean and jerk, use a lighter weight but for only a limited number of repetitions. The focus is on explosive movement, but only for six reps or fewer.

Testosterone-boosting Workout B
Exercise: Barbell front squat
Intensity+: 8-10 RM
Reps: 8-10
Tempo: Explosive
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4-6
Exercise: Bodyweight chip-ups
Intensity+: Bodyweight
Reps: To fatigue
Tempo #: Moderate
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4-6
Exercise: Barbell Romanian deadlift
Intensity+: 8-10 RM
Reps: 8-10
Tempo #: Moderate
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4-6
Exercise: Barbell push press*
Intensity+: 8-10 RM
Reps: 4-6
Tempo #: Explosive
Rest Interval: 1 min.
Set: 4-6
- Intensity: Perform 8-10RM and use a weight that can be lifted for a maximum of 10 reps. If it is possible to do more, increase the amount of weight used.
- # Tempo - This refers to the speed of movement, which should be one to two seconds in each direction.
For the barbell push press, use a lighter weight but for only a limited number of repetitions. The focus is on explosive movement, but only for six reps or fewer.



 by
by 



