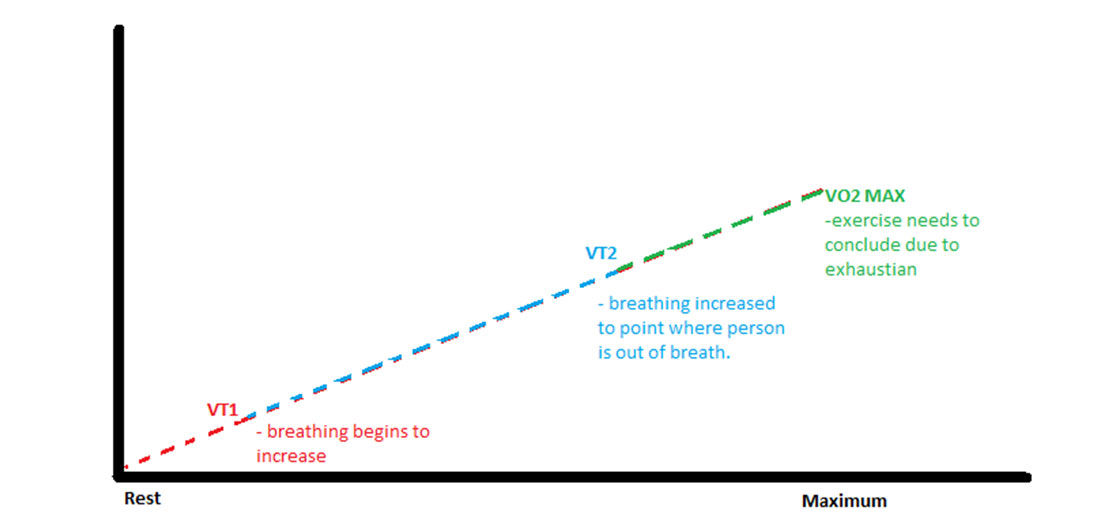
VT1 is called the first ventilatory threshold. It is a marker of intensity that can be observed in a person’s breathing at a point where lactate begins to accumulate in the blood. As the intensity of the exercise begins to increase, VT1 can be identified at the point where the breathing rate begins to increase. A person who is at VT1 can no longer talk comfortably,—but can still string together a few words—while exercising,.
Also observed by way of a person’s breathing during exercise is VT2, or the second ventilatory threshold. It is a higher marker of intensity than VT1. At VT2, lactate has quickly accumulated in the blood and the person needs to breathe heavily. At this rapid rate of breathing, the exerciser can no longer speak. The exercise duration will necessarily decrease due to the intensity level. VT2 can also be called the respiratory compensation threshold (RCT) and the onset of blood lactate accumulation (OBLA).
VO2 max is the maximal consumption of oxygen. It is the maximum capacity of the body to take in, transport, and use oxygen during exercise and reflects a person’s cardiorespiratory fitness. Measuring VO2 max is a laboratory procedure that requires equipment to analyze the amount of oxygen inhaled and the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled. This test will take an individual to the absolute maximum exercise intensity that he or she can achieve. Maximum heart rate can also be measured at this point.
A deconditioned person has a lower VO2 max than someone who is conditioned. As an exerciser becomes more conditioned, his or her VO2 max will increase.
Here is a simple way to picture a progression of these markers of exercise intensity (from least to most intense):
- Rest
- VT1 (breathing begins to increase)
- VT2 (out of breath, high intensity)
- VO2 max (exercise needs to conclude due to exhaustion)
A sedentary person will reach VT1, VT2, and VO2 max at a much lower intensities of exercise than a more physically active person. For example, an extremely deconditioned person may reach his or her VT1 while just walking. Conversely, a more conditioned person will reach these markers at a higher intensity. For example, he or she may reach VT1 at a running speed of 6 miles per hour.



 by
by